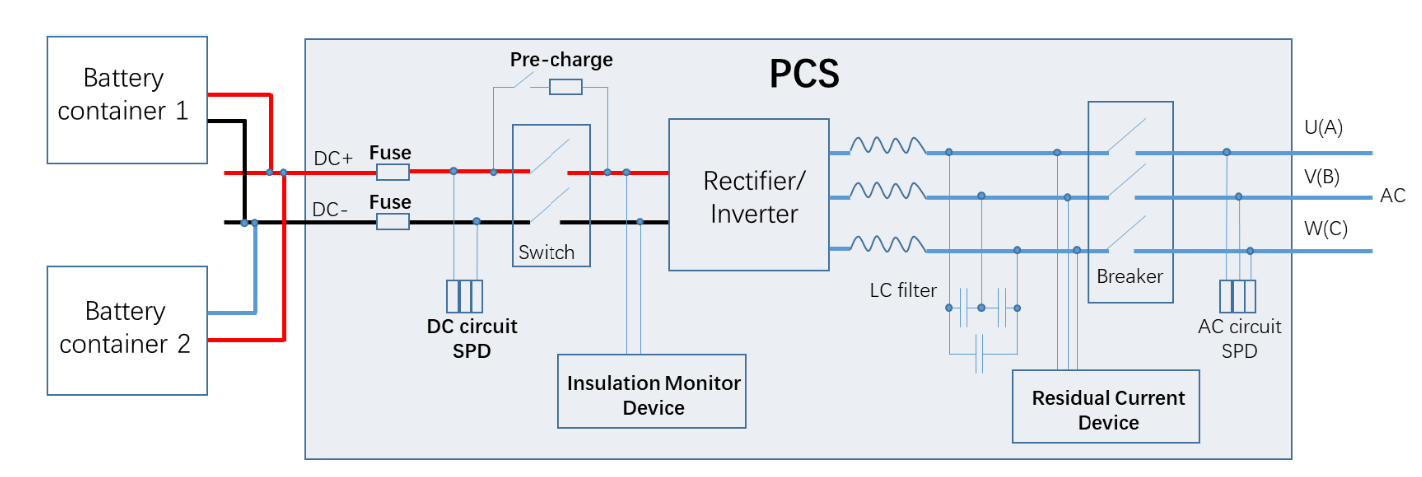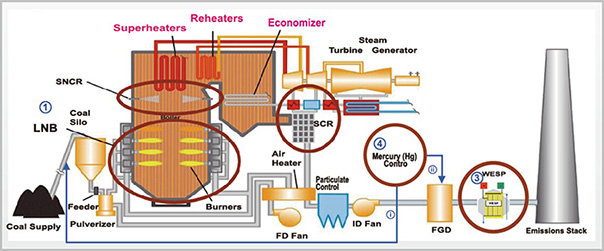
In 2013 Sunco International Inc. has successfully applied the first urea based furnace NOx reduction project in China that incorporates a combination of low NOx combustion, SNCR and SCR. This first of a kind NOx reduction project was installed on several industrial boilers – vertical slagging cyclone and corner-fired. We first incorporated advanced low NOx combustion modifications, with proven engineering technology and experienced designers using CFD simulation of combustion and secondary air. This system was designed to provide NOx reduction to reduce post-combustion reagent usage without deep staging. The low NOx combustion system was designed to accommodate easier optimization of the upper furnace urea injection with the SNCR/SCR system by providing the required flue gas temperature profiles and minimum CO. This SNCR system was provided along with SCR as a backup system for the SCR, in case there was a problem with the SCR injection system. Urea reagent delivery and dilution modules were utilized for both the SNCR and SCR.
An advanced urea pyrolysis technology for application with a downstream SCR was also demonstrated in this project. CFD flow field simulation and physical simulation were used to ensure the effectiveness of the urea lances, screens and mixing devices for urea pyrolysis and ammonia reactions with minimal slip as perspecification requirements. After commissioning, NOx emission less than 50mg/Nm3 were easily achieved, with ammonia slip of less than 1ppm. Significant modifications were required for the flue gas ducting in order to provide sufficient urea pyrolysis and mixing prior to the SCR catalyst bed. Optimization of the economizer and air pre-heater surfaces reduced exhaust gas temperature and improved boiler efficiency.
The following table summarizes the results of Sunco International Inc. advanced NOx reduction technology to a vertical slagging cyclone boiler.
|
|
Post-Retrofit
|
|||
|
NOx(mg/m³)
|
900
|
LNB
|
LNB+SNCR
|
LNB+(SNCR)+SCR
|
|
450
|
200
|
50
|
||
|
NOx Reduction |
/
|
50
|
78
|
95
|
|
Ammonia slip |
/
|
/
|
Less than 2.5
|
Less than 2.5
|