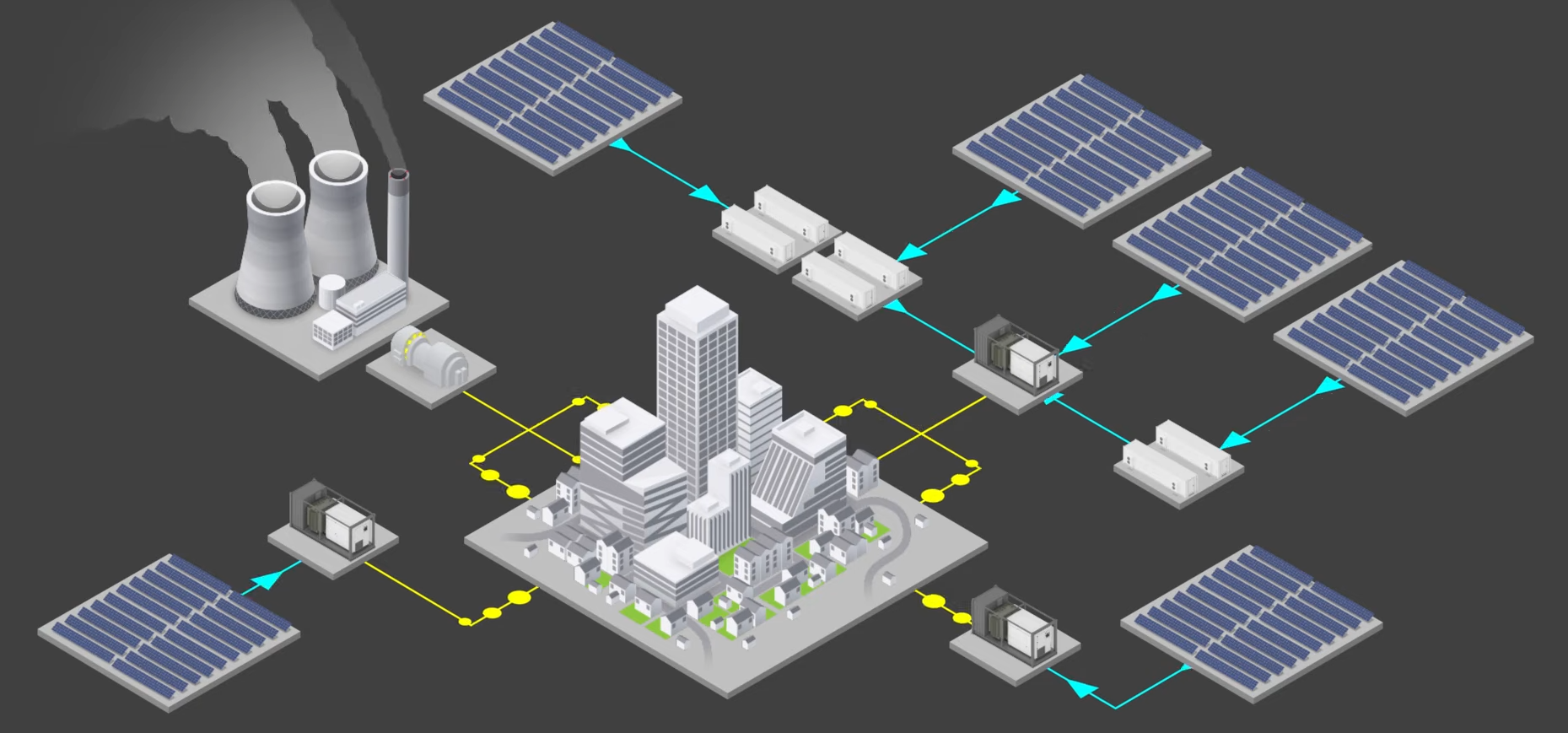
 The energy landscape is becoming increasingly complex with the integration of renewable resources, and one technology playing a pivotal role in this transition is the Battery Energy Storage System (BESS). The schematic provided outlines a sophisticated BESS setup, an integral component in modern energy systems for enhancing efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
The energy landscape is becoming increasingly complex with the integration of renewable resources, and one technology playing a pivotal role in this transition is the Battery Energy Storage System (BESS). The schematic provided outlines a sophisticated BESS setup, an integral component in modern energy systems for enhancing efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
Understanding BESS and Its Components
At its core, a BESS is designed to store energy in the form of electricity within a battery system. This energy can then be released back into the power grid as needed, offering a dynamic solution to the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. The diagram illustrates several key components:
-
Energy Storage Management System (ESMS): The brain of the operation, the ESMS oversees all aspects of the battery storage system, including inverter control, power conditioning, and battery management. It ensures optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the system.
-
Power Conditioning System (PCS): This section includes inverters that convert the stored DC power in the batteries to AC power suitable for the grid, managing the quality and compatibility of the electricity being fed into the system.
-
Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors and maintains the battery status, including voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge, ensuring the batteries operate within safe and efficient parameters.
-
AC Breakers and Reclosers: These components protect the BESS by interrupting the current flow in the event of an overload or fault, and automatically closing the circuit once normal conditions are restored.
-
Substation with CT/PT: The substation serves as a point of connection to the grid and includes current transformers (CT) and potential transformers (PT) for metering and monitoring the electricity flow.
The Benefits of BESS in Modern Grids
The integration of a BESS offers a multitude of benefits to the grid:
-
Peak Shaving: By releasing stored energy during peak demand times, BESS can alleviate the strain on the grid and reduce the need for peaking power plants.
-
Load Leveling: BESS can balance the load by storing excess energy during low demand and releasing it during high demand, leading to more stable and efficient grid operation.
-
Renewable Integration: As renewables are variable, BESS can store surplus energy when production is high and supply energy when it's low, thus smoothing out the supply.
-
Frequency Regulation: BESS can quickly respond to grid frequency changes, helping maintain the required 50/60 Hz, which is crucial for grid stability.
-
Emergency Backup: In case of power outages, BESS can provide immediate supply, enhancing grid resilience.
Conclusion: Energizing the Future
The Battery Energy Storage System is a cornerstone in the modernization of power grids, especially as we shift towards more renewable energy sources. The system's ability to store and manage energy effectively addresses many challenges posed by the fluctuating nature of renewable power, and its integration is essential for creating a more reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy future.
